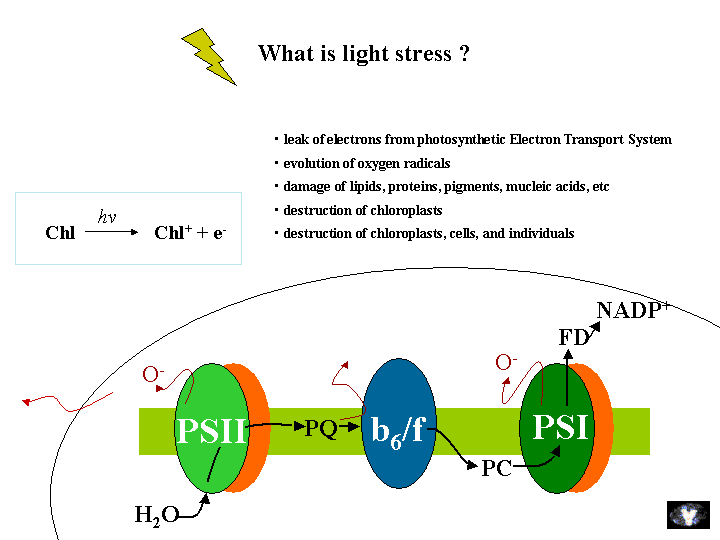
What is light stress ?
The photosynthesis is a series of energy transformation,
starting from capturing light energy to production of sugars, in which
chemical energy is stored in a stable way. The first step is
light-driven electrion transport at the thylakoid membrane, and by this
process, NADP is reduced and the
thylakoid membrane is charged. The membrane charge is then utilized to
produce
ATP by the coupling factor complex.
Under weak light conditions (called low light), plants
produce
small amount of NADPH and ATP, so the growth is slow. If the light
quantity
increases, the Electron Transport System becomes more active to
synthesize
more NADPH and ATP, making plants happier.
However, the Electron Transport System has a capasity for its process.
When light intensity becomes higher than the capacity, electron
overflows from the Electron Transport System. Oxygen radicals are known
to evolve mainly from PSI and damage chloroplast components. Under
severe conditions, plants die due to exposure to intense light (called
high light). If you imagine a graph of light intensity for X-axis and
plants' happiness for Y-axis, it
would be like this (Fig. 1.2
).
In summary, light stress occurs when plants capture excess
or
unmanagable amount of light for the ETS.