2.1 Lider
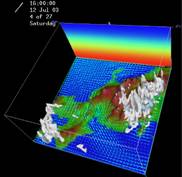
The lider developed in our group is a Laser remote-sensing system to observe the distribution of water particles or ice crystals in the upper sky.
2.2 Whole-Sky Camera
The fish-eye camera captures the clouds' distributions continuously. The observed continuous images of the clouds are used also for the tracking of clouds for evaluation of shading or flickering of solar rays due to clouds.
2.3 Solar Spectrum Radiometer
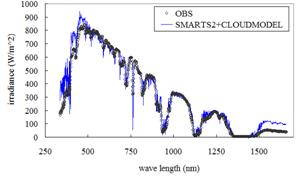
Solar Spectrum Radiometer is installed and operated at Gifu University by Japan Weather Association. The observed data is used also for the development of the solar spectrum database.
2. Development of observation systems for the solar irradiation and their applications
The field observations correct data for the development and the evaluation of the Meteorological and Solar Irradiation Models.
1. Development of Meteorological and Solar Irradiation Models
The predicted actual solar generation is more useful information than the solar panel specification (Energy rating) for consumers to make their decisions to install solar systems. We are developing numerical simulation models to forecast high accurate actual solar generation. The forecast data is also applied for the planning of the advanced Smart Grid.
1.1 Meso-scale Meteorological Model for Solar Irradiations
We are developing a meteorological
forecasting system for the solar generation by improving the operating weather
forecasting model. We are the only Japanese University that is publishing the
high-resolution daily weather forecasting, so-called "pinpoint
forecasting", under the license of the Japanese Meteorological Agency.
The
model is specialized for the prediction of the solar radiation by making
possible to evaluate the diameter-distributions of cloud-particles that
influence directly the transmission and scattering properties of the
atmosphere. This model supplies appropriate predicted weather conditions to the
following Solar Spectrum Infrarate Model.
Solar Spectrum Infrarate Model is developed for forecasting the spectrum intensity of solar radiation by applying the forecasted weather information computed by the Meso-scale Meteorological Model. This model can evaluate the solar spectrum in the field: for example, strong sunshine in clear days, dark sunshine in cloudy sky, and bright colors of the sunsets. The solar generation in the field by any photovoltaic systems with different spectrum characteristics can be predicted with this Solar Spectrum Infrarate Model.
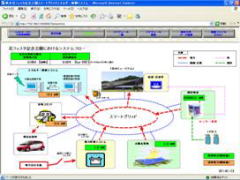
3. Operation of an Advanced Smart Grid containing Photovoltaic systems
Output of solar generation systems depend on the weather condition and therefore are unstable. The developing advance Smart Grid can supply stable electric energy to the consumers by controlling not only electric appliances as the ordinal Smart Grid does, but also generation systems. Solar energy systems are contained in the Grid, and the forecasting data of their generation is used for planning the Grid operation. The Smart Grid field experiment is running at the Flower Festival Commemorative Park, Gifu.